Corsi-Block Tapping Test - CORSI - 1 Year License
Model 64047
Assessment of the capacity of the visual short-term memory and of the implicit visual-spatial learning. Applicable to people aged 6 years and over.
Test Overview
Neuropsychological studies prove that the immediate block span can depict deficits that are not assessed by common tests for the registrations of the verbal memory span.
Main Areas of Application
- Clinical psychology
- Neuropsychology
Theoretical Background
Tests, which examine the memory span, mainly focus on the short-term memory that is provided with a limited capacity only. The assessment of the memory span is an important factor. The short- term memory is provided with a verbal subsystem as well as a visual-spatial subsystem. These subsystems can be damaged separately from each other by brain traumata, which is a proof of their - almost complete -independency. The Block-Tapping-Test for the assessment of the immediate block span (UBS) assesses the capacity of the visual-spatial subsystem within the short-term memory. The theoretical background is characterized by Baddeley's concept of the working memory. The Block-Tapping-Test for the registration of the supra-block span (SBS) goes beyond the assessment of the short- term memory: sequences are used that exceed the respondent's visual memory span and thus make necessary to acquire specific learning processes. This implies to learn a frequently repeated sequence that is embedded into a pool of sequences with equal length. The respondent does not know that a sequence is repeated in the items that are presented: implicit learning is being operationalized. The test registers the number of repetitions until the relevant sequence is imitated correctly. It was designed in the context of neuropsychological experiments of the right temporal lobe.
Administration
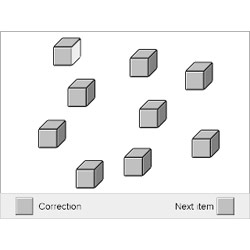
The monitor displays 9 randomly positioned dice. A hand points on a certain number of these dice. The respondent is then asked to point at the dice in the same order. The number of dice increases always when 3 items are answered correctly, while the test run is cancelled when he or she answers three subsequent items incorrectly.
In order to assess implicit visual-spatial learning (supra-block-span), first the immediate block-span is calculated. Then the number of dice is increased by one for the next couple of items. The test consists of 24 items, containing a sequence that is repeated eight times (target sequence). The test is over as soon as the respondent reproduces the target sequence correctly.
Test Forms
Four test forms are available. Two of these measure the immediate block span of adults (S1) and children and clinical patients (S2). The other two measure the immediate and the supra-block span of adults (S3) and children and clinical patients (S4). Test forms S2 and S4 contain sequences of between 2 and 8 blocks, while forms S1 and S3 contain sequences of between 3 and 8 blocks.
Scoring
The variable immediate block span operationalises the visuo-spatial memory span. It indicates the longest se-quence length that has been reproduced correctly at least once. The variable supra-block span operationalises implicit visuo-spatial learning. It indicates the number of attempts made by the respondent before the target sequence was correctly reproduced.
Reliability
The reliability of the test is between r=0.81 and r=0.89, depending on the test form used.
Validity
The block-tapping test is frequently referred to in the neuropsychological literature as a test of visuo-spatial memory span and is also widely used in a clinical context. Studies of brain-damaged patients using the blocktapping test demonstrate that the test assesses a visuo-spatial function of short-term memory that is independent of the verbal subsystem.
Norms
Provision of conventional norms is inappropriate, since the variable can assume only seven different values. Cut-off scores are therefore calculated instead. If a respondent's block span lies below the cut-off score, a footnote to this effect is included in the results.
Testing Time
Between 10 and 15 minutes (including instruction and practice phase), depending on test form.
VTS System Overview
The Schuhfried VTS enables computer-assisted application of a large number of highly diverse psycho-diagnostic tests and measuring procedures. In developing the system much emphasis was placed on transparent structure and largely uniform design. It is therefore simple to operate and easy to understand and does not require any special computer skills.
The VTS basic module is required for administration of any of the available tests.
The Schuhfried VTS supports the administration of both single tests and test batteries. Many of the single tests are available in different test versions. These test versions may differ, for example, in terms of test duration or difficulty or may be parallel forms. They are characterized by different parameters reflecting specific test requirements. They have been designed for administration to a specific population (e.g. psychiatric patients, children, etc.) or for special measuring purposes (e.g. repeated measurements). Test batteries are compiled from the available single tests and test versions.
